Knee Replacement Surgery
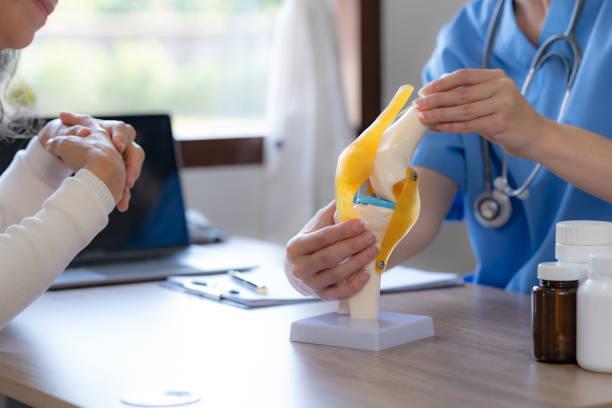
Knee replacement surgery (also known as knee arthroplasty) is a common and highly effective procedure used to relieve pain and improve function in individuals suffering from severe knee arthritis or damage to the knee joint. The goal of the surgery is to replace the damaged parts of the knee with artificial components (prosthetics) to restore movement, relieve pain, and improve the patient's quality of life.Why Knee Replacement Surgery is NeededKnee replacement surgery is typically recommended for people who have severe knee pain or disability that doesn't improve with non-surgical treatments such as medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes. Common conditions that can lead to the need for knee replacement include:1. OsteoarthritisThe most common cause for knee replacement surgery. Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage in the knee wears down, leading to bone-on-bone contact, pain, and stiffness.2. Rheumatoid ArthritisAn autoimmune condition that causes inflammation in the joints, leading to cartilage damage and knee pain.3. Post-Traumatic ArthritisArthritis that develops after a knee injury or fracture. Damage to the knee joint can lead to long-term degeneration.4. Knee DeformitiesConditions such as bowed legs (varus deformity) or knock knees (valgus deformity) may require knee replacement surgery to realign the joint.5. Knee FracturesSevere fractures of the knee that cannot be repaired with internal fixation or other treatments may also require knee replacement surgery.Types of Knee Replacement Surgery1. Total Knee Replacement (TKR)Total knee replacement is the most common type of knee surgery. It involves replacing the entire knee joint, including the femur (thigh bone), the tibia (shin bone), and the patella (kneecap).Procedure:The surgeon removes the damaged or worn-out portions of the femur, tibia, and sometimes the patella.These parts are replaced with artificial components made from materials such as metal, plastic, or ceramic.Indications: Severe arthritis, joint deformities, and joint damage that cannot be treated with less invasive methods.2. Partial Knee Replacement (PKR)A partial knee replacement is a less invasive surgery in which only the damaged portion of the knee joint is replaced. The rest of the knee joint is left intact.This is typically an option for people with unicompartmental osteoarthritis, where only one side of the knee (medial, lateral, or patellofemoral compartment) is affected.Procedure:The surgeon removes the damaged part of the joint and replaces it with a prosthetic component, while the healthy parts of the joint are preserved.Indications: Unicompartmental arthritis, where only one part of the knee is severely damaged.3. Bilateral Knee ReplacementBilateral knee replacement refers to the simultaneous or staged replacement of both knees. This may be an option for people who suffer from severe arthritis or damage in both knees.This can either be performed during one surgery (simultaneous) or in two separate surgeries, typically spaced months apart (staged).4. Complex or Revision Knee ReplacementRevision knee replacement is a second surgery to replace a knee prosthesis that has worn out, loosened, or failed after an initial knee replacement.This is often necessary if the artificial components become loose, infected, or if there is significant wear or fracture of the implant.The Knee Replacement ProcedureThe surgical procedure typically involves the following steps:Anesthesia:The surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia (where you are fully asleep) or regional anesthesia (such as a spinal block, where only the lower body is numbed).Incision:The surgeon makes an incision over the knee to access the joint. The size of the incision depends on whether it’s a total or partial knee replacement.Bone Preparation:The damaged surfaces of the femur, tibia, and possibly the patella are carefully removed.Prosthesis Insertion:Artificial components (prostheses) made of metal, plastic, and sometimes ceramic are inserted into the knee to replace the damaged bone surfaces. The new components are designed to mimic the natural motion of the knee.Closing the Incision:Once the prosthetic components are in place, the surgeon checks the knee for proper alignment and movement before closing the incision with sutures or staples.Postoperative Care:The patient is moved to a recovery room and monitored for any complications. Pain management, physical therapy, and proper care are essential for a successful recovery.Recovery After Knee Replacement Surgery1. Hospital StayAfter surgery, patients typically stay in the hospital for 1 to 4 days, depending on how well they are recovering.During this time, the medical team will monitor vital signs, pain levels, and ensure that there are no signs of complications (e.g., infection, blood clots).2. Physical TherapyPhysical therapy begins immediately after surgery to help restore strength, mobility, and range of motion to the knee. The focus will be on gradually increasing the knee's movement and flexibility.Exercises typically include bending and straightening the knee, walking with a walker or crutches, and strengthening surrounding muscles.Full rehabilitation may take 6 months to 1 year, depending on the individual’s health, the type of knee replacement, and adherence to physical therapy.3. Pain ManagementPain relief after knee replacement surgery typically involves a combination of medications (such as acetaminophen, NSAIDs, or stronger opioids if necessary) and ice or elevation to reduce swelling.Regional anesthesia or a nerve block can provide pain relief during the first few days after surgery.4. Activity RestrictionsEarly recovery involves avoiding excessive weight-bearing and high-impact activities that could stress the knee implant.After the initial healing period, patients are generally encouraged to walk, swim, and engage in low-impact exercises like cycling to help maintain joint function.5. Long-Term RecoveryFull recovery typically takes 6 to 12 months. During this period, it’s essential to follow your surgeon’s guidance on activity levels, pain management, and physical therapy to achieve the best outcome.While the knee will feel better and be more functional, patients should avoid high-impact activities like running or jumping that could wear out the artificial knee joint.Benefits of Knee Replacement SurgeryPain Relief:Knee replacement can eliminate or significantly reduce knee pain caused by arthritis, fractures, or deformities, allowing patients to return to daily activities.Improved Functionality:After recovery, many patients experience improved mobility, making activities such as walking, climbing stairs, and getting in and out of chairs easier.Enhanced Quality of Life:Many patients report a better quality of life after knee replacement surgery, including increased ability to participate in recreational activities, improved sleep, and better overall physical health.Potential Risks and Complications of Knee Replacement SurgeryAs with any surgery, knee replacement carries some risks, including:Infection:An infection at the surgical site or in the prosthesis.Blood Clots:The formation of blood clots in the legs (deep vein thrombosis) or lungs (pulmonary embolism) can be a serious complication.Implant Loosening or Failure:The artificial knee components may wear out or become loose over time, requiring revision surgery.Nerve or Blood Vessel Damage:Although rare, damage to surrounding nerves or blood vessels can occur during surgery.Stiffness or Reduced Range of Motion:Some patients may experience stiffness in the knee joint post-surgery, which can be addressed with therapy.ConclusionKnee replacement surgery can be life-changing for those suffering from severe knee pain and dysfunction due to arthritis, injury, or deformity. By replacing the damaged parts of the knee joint with prosthetic components, knee replacement surgery aims to restore mobility, alleviate pain, and improve quality of life. Whether you are undergoing a total knee replacement, partial knee replacement, or revision surgery, proper recovery and rehabilitation are crucial for the best outcomes.Would you like more information on a specific aspect of knee replacement, such as preparation, recovery, or post-surgery care? Let me know!
READ MORE